Entropic force on a Polymer
![]() Several micro-manipulation techniques, such as Atomic Foce Microscopy, measure forces required to unravel specific (mostly bio-) polymers.
Several micro-manipulation techniques, such as Atomic Foce Microscopy, measure forces required to unravel specific (mostly bio-) polymers.
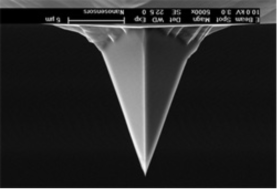
![]() What is the entropic force on a uniform (phantom or self-avoiding) polymer?
What is the entropic force on a uniform (phantom or self-avoiding) polymer?
The answer depends on whether the bounding surfaces are attractive or repulsive:
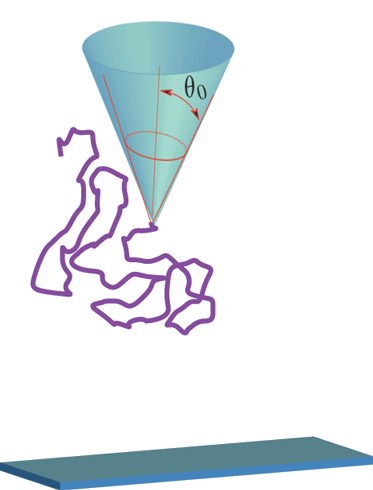
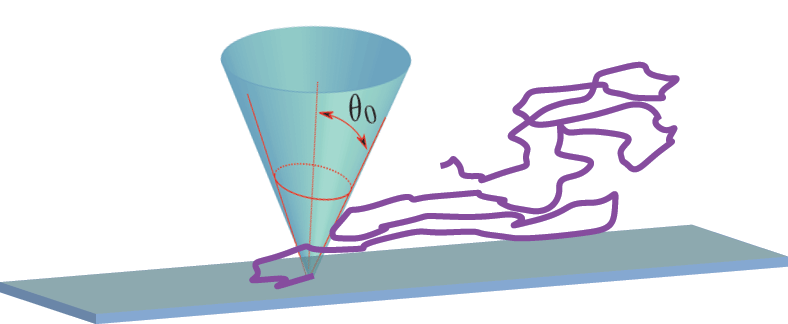
![]() Attractive Surface and Repulsive tip
Attractive Surface and Repulsive tip 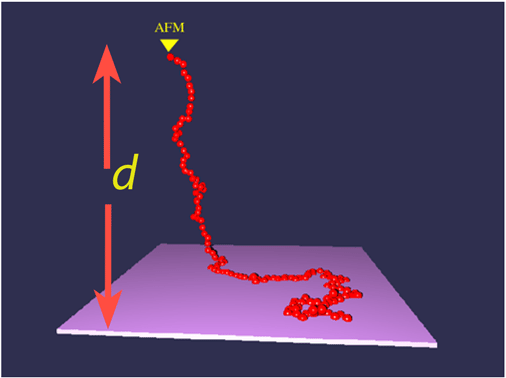
The polymer exerts an attractive force, equal to the free energy gain per unit length:
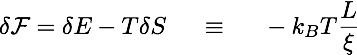
The free energy gain vanishes at the depinning transition. Close to this transition:
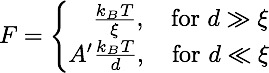
The coefficient A' depends on the shape of the tip, and is universal for scale free shapes.
![]() Repulsive Surface and tip
Repulsive Surface and tip 
Dimensional analysis suggests:
Work done in moving the tip (with polymer attached) away from the surface is
 =>
=> 
This work can be related to the difference in free energies, as
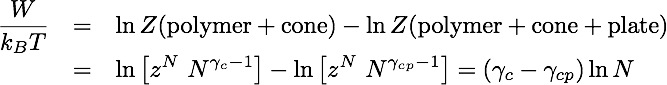
Comparing the two expressions yields
![]()
"Entropic force of polymers on a cone tip," M. F. Maghrebi, Y. Kantor, M. Kardar, EPL 96, 66002 (2011)