The Neural
Control of Visually Guided Eye Movements
C. Cortical Mechanisms of Visually Guided Saccadic Eye Movements
The effects of one pharmacological agent is described here when applied
to area V1 and to the frontal eye fields (FEF). The agent is bicuculline
which is a GABA antagonist. In other words its administration releases
the area from GABAergic inhibition.
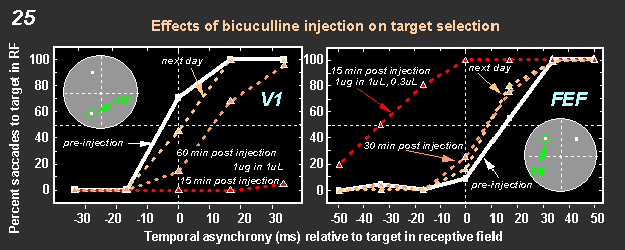
Figure 25
shows the effects of bicuculline injection into areas V1 and FEF.
Opposite effects were found in these two areas. In V1 administration of
bicuculline causes a major interference in the selection of the target
placed into the receptive field of the neurons affected. By contrast,
administration of bicuculline into the FEF produced dramatic facilitation.
This effect is similar to that reported previously in the superior colliculus
by Hikosaka and Wurtz (J Neurophysiol 1985; 53(1): 266-91).
|
